Which part of the respiratory system is responsible for regulate breathing rate and depth?
A. Bronchi
B. Alveoli
C. Diaphragm
D. Trachea
The diaphragm is responsible for regulang breathing rate and depth. It is a dome-shaped muscle located at the botom of the chest cavity that contracts and relaxes to help move air in and out of the lungs.
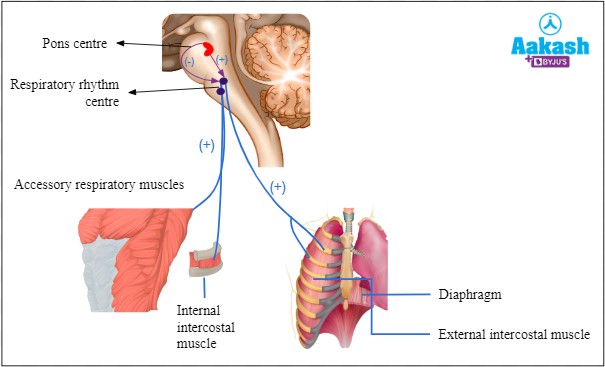
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.