Which of the following hormones is responsible for regulating the body's metabolism and energy levels?
A. Estrogen
B. Progestin
C. Thyroxine
D. Androgen
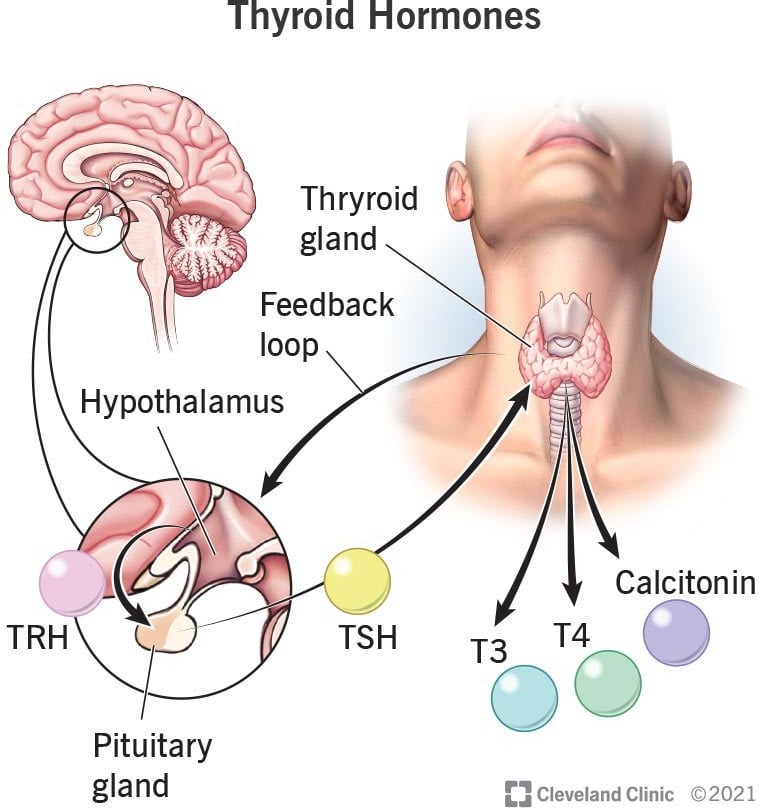
The correct answer is choice C. Thyroxine.
Thyroxine (T4) is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that controls your body’s metabolism, the process in which your body transforms the food you eat into energy.
Choice A, Estrogen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
Choice B, Progestin, is not the correct answer because it is a synthetic form of progesterone used in hormonal birth control and hormone replacement therapy.
Choice D, Androgen, is not the correct answer because it is a hormone responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is C.