Which of the following are examples of homeostatic mechanisms?
A. Increasing heart rate when blood pressure is low, Consuming excess calories to gain weight
B. Lifting weights to increase muscle mass
C. Shivering when the body temperature falls
D. Shivering when the body temperature falls, Secreting insulin to decrease blood sugar concentration, Increasing heart rate when blood pressure is low
Homeostatic mechanisms are involuntary actions by organs, glands, tissues and cells to maintain balance within the body. For example, if a person becomes dehydrated, the kidneys will retain fluid by decreasing urine output.
Consuming excess calories and lifting weights are not involuntary actions, nor do they maintain the body in its baseline state. Rather, they are actions specifically taken to move the body away from its baseline.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is D.

 AC + B. Double replacement reactions have the general form of AB + CD→
AC + B. Double replacement reactions have the general form of AB + CD→ AD + CB. Synthesis reactions have the general form of A + B →
AD + CB. Synthesis reactions have the general form of A + B → AB. Decomposition reactions have the general form AB→
AB. Decomposition reactions have the general form AB→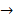 A+B.
A+B.
