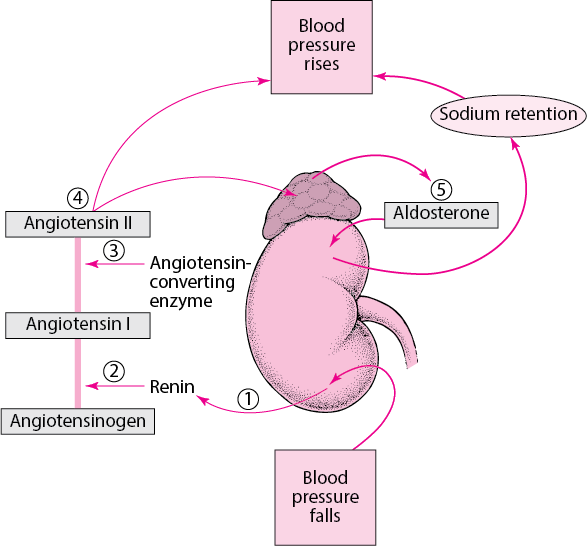
What is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants?
A. Chlorophyll a
B. Chlorophyll b
C. Carotenoids
D. Anthocyanins
Chlorophyll a is the primary pigment responsible for photosynthesis in plants. It is a green pigment that is essential for capturing light energy from the sun and converting it into chemical energy that can be used by the plant. Chlorophyll a absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum, and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic green color
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll that is also involved in photosynthesis, but it is not as abundant as chlorophyll a. Chlorophyll b absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and orange parts of the spectrum and reflects yellow-green light.
Carotenoids are pigments that are present in many plants and are involved in photosynthesis as well as protecting the plant from damage caused by excess light. Carotenoids are responsible for the orange, yellow, and red colors of many fruits and vegetables.
Anthocyanins are pigments that give plants their red, purple, and blue colors. While they are not directly involved in photosynthesis, they play a role in atracting pollinators and protecting the plant from damage caused by UV radiation.
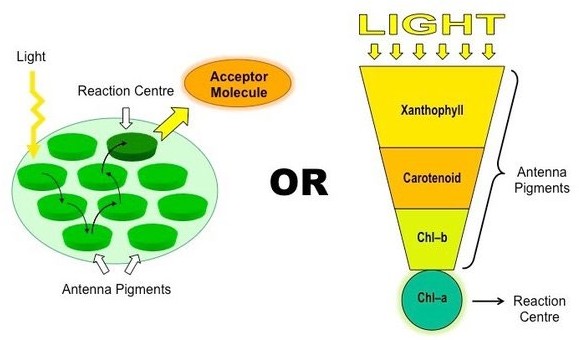
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.