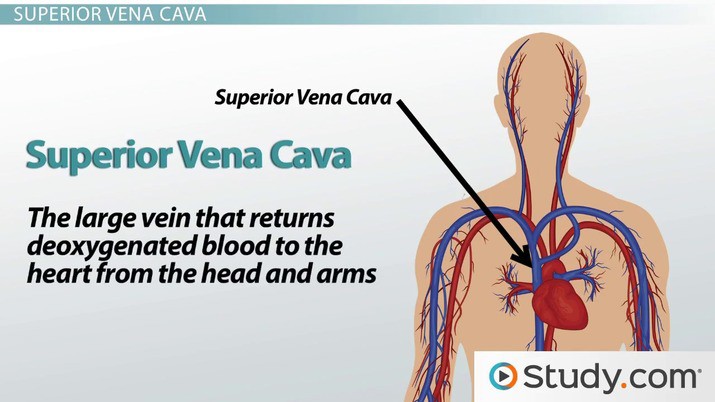
What is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart?
A. Superior vena cava.
B. Inferior vena cava.
C. Pulmonary vein.
D. Renal vein.
The correct answer is choice A.
The superior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body that returns deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice B is incorrect because the inferior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart.
Choice C is incorrect because the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Choice D is incorrect because the renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.