What is hydrogen bonding?
A. The attraction between the relatively positive areas of one molecule and the relatively negative areas of another molecule.
B. The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules.
C. The attraction between two nonpolar molecules.
D. The attraction between two ionic molecules.
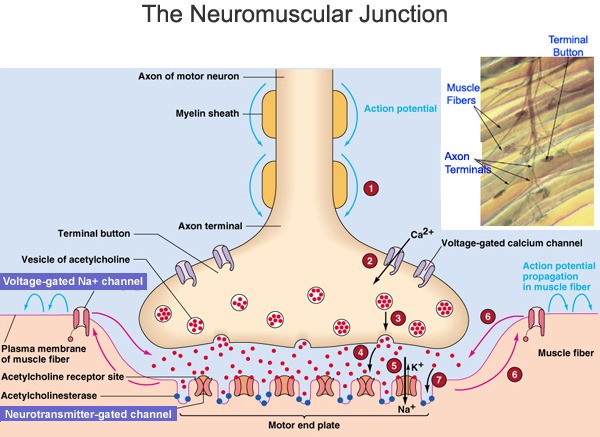
Hydrogen bonding is an interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
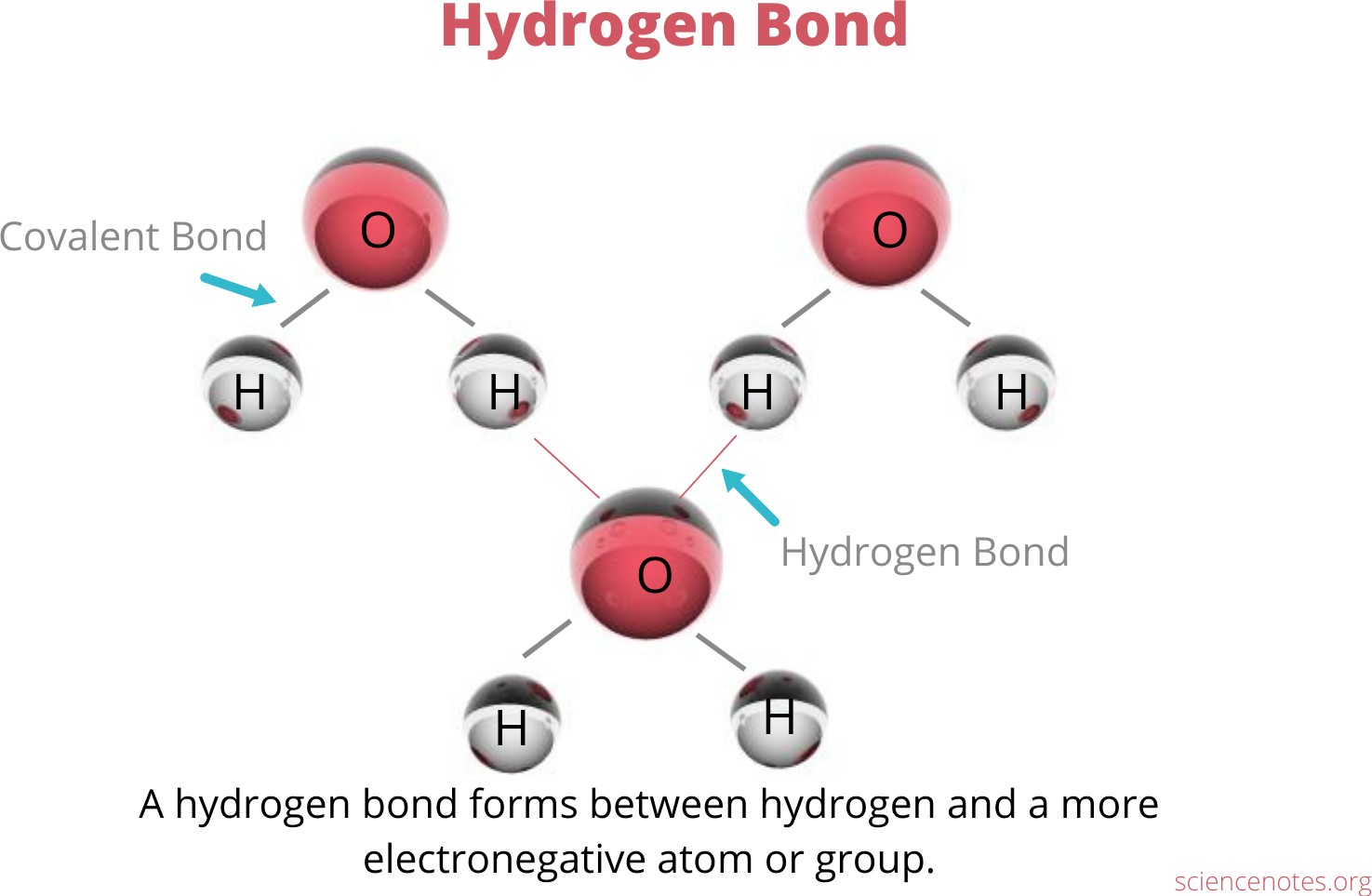 |
One atom of the pair (the donor), generally a fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen atom, is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom, whose electrons it shares unequally; its high electron affinity causes the hydrogen to take on a slight positive charge.
The other atom of the pair (the acceptor), also typically F, N, or O, has an unshared electron pair, which gives it a slight negative charge.
Mainly through electrostatic attraction, the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom, forming a bond.
Choice B) The repulsion between the positive and negative charges of two molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves attraction, not repulsion.
Choice C) The attraction between two nonpolar molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules.
Choice D) The attraction between two ionic molecules is incorrect because hydrogen bonding involves polar molecules and not ionic molecules.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is A.