Blood oxygen levels are most likely low when blood _____.
A. leaves the aorta
B. fills the right atrium
C. reaches body tissues
D. flows through arteries
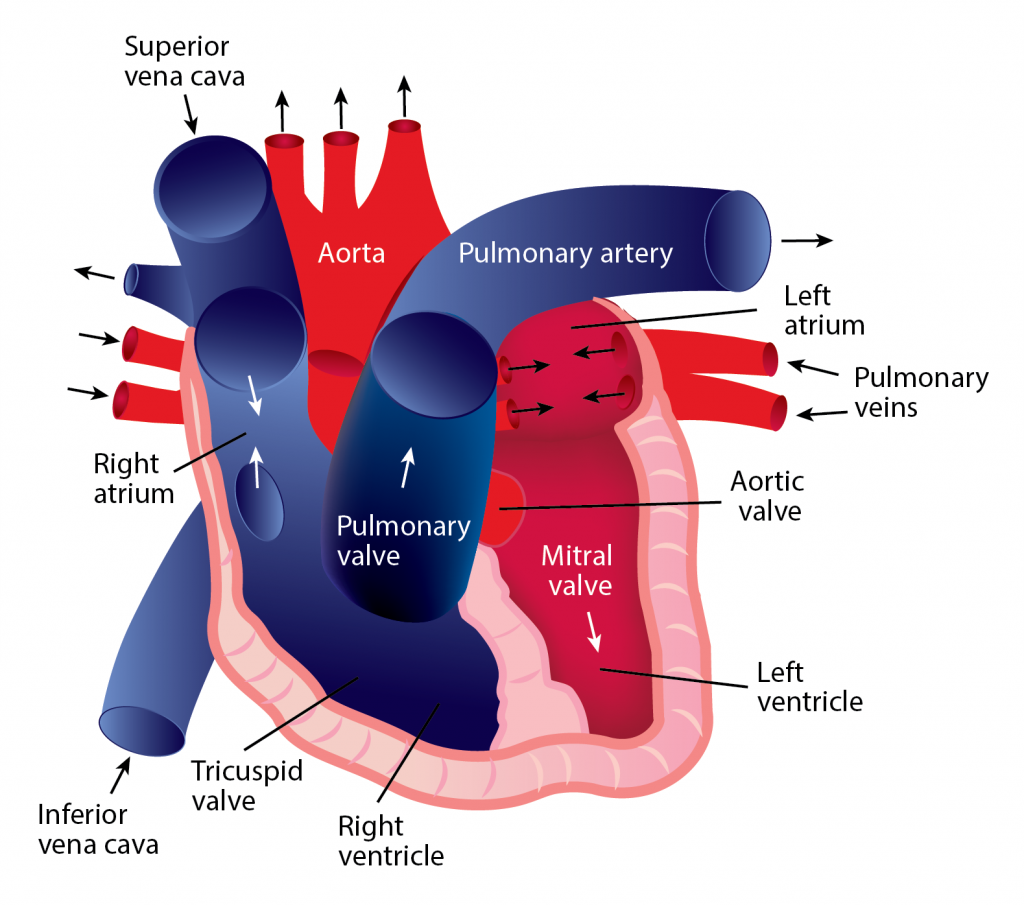
Blood continually flows in one direction, beginning in the heart and proceeding to the arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. When blood reaches the capillaries, exchanges occur between blood and tissues. After this exchange happens, blood is collected into venules, which feed into veins and eventually flow back to the heart’s atrium. The heart must relax between two heartbeats for blood circulation to begin.
Two types of circulatory processes occur in the body:
Systemic circulation
- The pulmonary vein pushes oxygenated blood into the left atrium.
- As the atrium relaxes, oxygenated blood drains into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. 3. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
- Blood travels through the arteries and arterioles before reaching the capillaries that surround the tissues.
Pulmonary circulation
- Two major veins, the Superior Vena Cava and the Inferior Vena Cava, brings deoxygenated blood from the upper and lower half of the body.
- Deoxygenated blood is pooled into the right atrium and then sent into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve, which prevents blood from flowing backward.
- The right ventricle contracts, causing the blood to be pushed through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery.
- Deoxygenated blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
Therefore, the Correct Answer is B.